| Submit | All submissions | Best solutions | Back to list |
PHIDIAS - Phidias |
Famous ancient Greek sculptor Phidias is making preparations to build another marvellous monument. For this purpose he needs rectangular marble plates of sizes W1 x H1, W2 x H2 ... WN x HN.
Recently, Phidias has received a large rectangular marble slab. He wants to cut the slab to obtain plates of the desired sizes. Any piece of marble (the slab or the plates cut from it) can be cut either horizontally or vertically into two rectangular plates with integral widths and heights, cutting completely through that piece. This is the only way to cut pieces and pieces cannot be joined together. Since the marble has a pattern on it, the plates cannot be rotated: if Phidias cuts a plate of size A ? B then it cannot be used as a plate of size B ? A unless A = B. He can make zero or more plates of each desired size. A marble plate is wasted if it is not of any of the desired sizes after all cuts are completed. Phidias wonders how to cut the initial slab so that as little of it as possible will be wasted.
As an example, assume that in the figure below the width of the original slab is 21 and the height of the original slab is 11, and the desired plate sizes are 10 x 4, 6 x 2, 7 x 5, and 15 x 10. The minimum possible area wasted is 10, and the figure shows one sequence of cuts with total waste area of size 10.
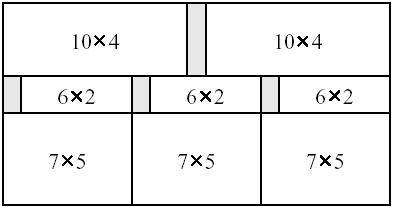
Your task is to write a program that, given the size of the original slab and the desired plate sizes, calculates the minimum total area of the original slab that must be wasted.
Input
t - the number of test cases, then t test cases follow [t ≤ 20].
The first line of each test case contains two integers: first W, the width of the original slab, and then H, the height of the original slab. The second line contains one integer N: the number of desired plate sizes. The following N lines contain the desired plate sizes. Each of these lines contains two integers: first the width Wi and then the height Hi of that desired plate size (1 ≤ i ≤ N). [1 ≤ W ≤ 600, 1 ≤ H ≤ 600, 0 < N ≤ 200, 1 ≤ Wi ≤ W, and 1 ≤ Hi ≤ H.]
Output
For each test case output one line with a single integer: the minimum total area of the original slab that must be wasted.
Example
Input: 1 21 11 4 10 4 6 2 7 5 15 10 Output: 10
| Added by: | Roman Sol |
| Date: | 2005-05-20 |
| Time limit: | 21s |
| Source limit: | 30000B |
| Memory limit: | 1536MB |
| Cluster: | Cube (Intel G860) |
| Languages: | All except: NODEJS PERL6 VB.NET |
| Resource: | IOI 2004 |
hide comments
|
|||||
|
2015-12-31 11:42:38 ashish kumar
top down 8.07 sec bottom up 1.84 sec what a huge difference ....! |
|||||
|
2015-11-29 16:02:44
easy O(w*h*n)..will pass...! |
|||||
|
2015-03-26 16:42:49 kp
where are we getting the plate sized 15 * 10 in the test case? got it. (Y) Last edit: 2015-03-26 16:45:06 |
|||||
|
2015-03-07 17:26:51 rajat arora
the solutions are wrong in sense that they dont take into account that the desired plates can be obtained in reversed fashion i.e in above example you cant make a cut of dimension 4*10 though 10*4 is allowed. Last edit: 2015-03-07 17:27:16 |
|||||
|
2013-05-30 13:14:28 Aradhya
well i m wondering if a O ( n ^ 2 ) solution exists o.O |
|||||


 RSS
RSS