| Submit | All submissions | Best solutions | Back to list |
PROG0311 - Cellophane |
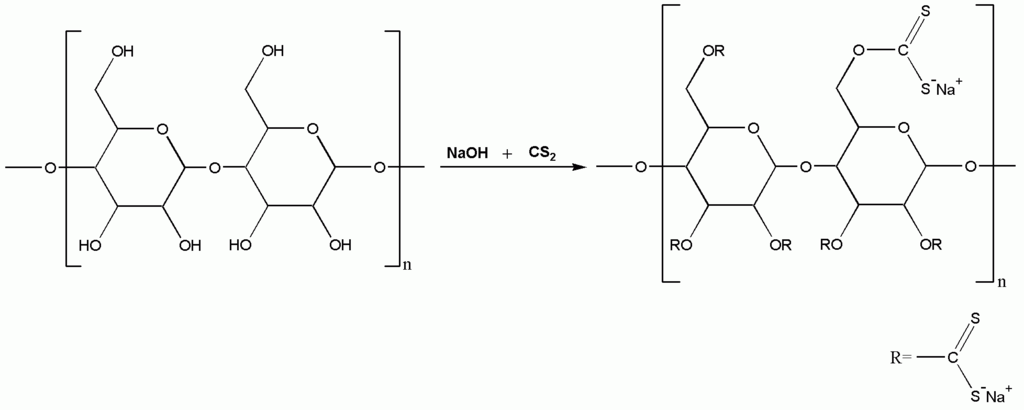
Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Cellulose fiber from wood, cotton or hemp is dissolved in alkali and treated with carbon disulfide to make a solution called viscose. This solution is then extruded through a slit into a bath of dilute sulfuric acid and sodium sulfate to reconvert the viscose into cellulose. The film is then passed through several more baths, one to remove sulfur, one to bleach the film, and one to add glycerin to prevent the film from becoming brittle.
Cellophane was invented by Swiss chemist Jacques E. Brandenberger. It took ten years for Brandenberger to perfect his transparent film, before cellophane was patented in 1912. Cellulose film has been manufactured continuously since the mid-1930s and is still used today. As well as packaging a variety of food items, there are also industrial applications, such as as a base for such self-adhesive tapes (including Sellotape and Scotch Tape) and as a semi-permeable membrane in a certain type of battery. Cellophane sales have dwindled since the 1960s, due to alternative packaging options and due to the polluting effects of carbon disulfide and other by-products of the process used to make viscose.
Assignment
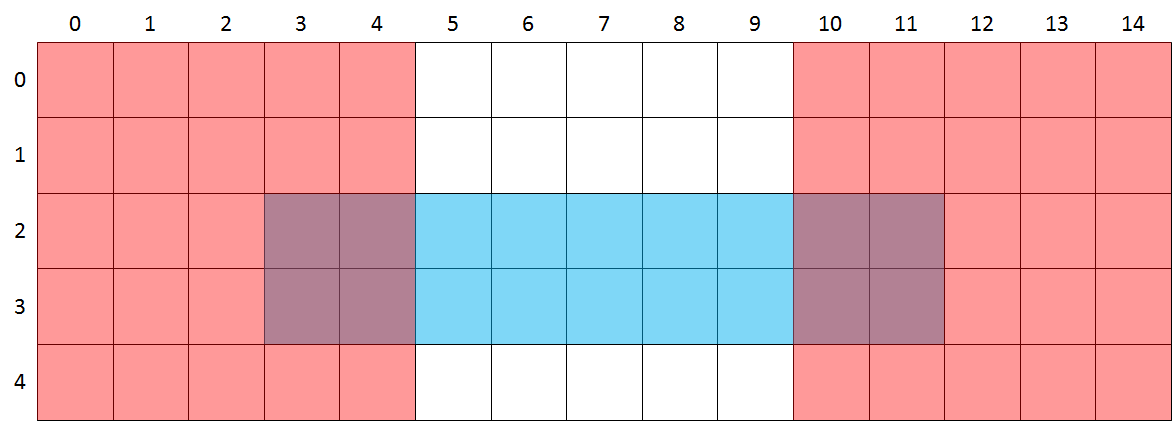
A rectangular grid is drawn on a flat surface — for example a window or a lighted plate used by doctors to view x-ray images. The rows of the grid have been numbered left to right starting from zero, as do the columns from top to bottom. Some rectangular cellophane sheets are attached to the surface, with each sheet exactly covering some of the squares in the grid. These transparent sheets are either colored red or blue. If a square is covered by one or more red sheets it is colored red. If a square is covered by one ore more blue sheets it is colored blue. If a square is covered by at least one read and at least one blue sheet, it is colored purple.
Determine how many purple squares you get if the grid on a surface is covered by a given series of red and blue sheets. This is done in the following way.
- Write a function purple that takes a list of the positions of a series of cellophane sheets. Each sheet is represented by a tuple containing five elements. The first two elements are integers that indicate the column and row number of the square in the grid that is covered by the top left corner of the sheet. The next two elements are integers that indicate the width and height of the sheet, expressed as a number of squares. The final element is a string that indicates the color of the sheet: R (red) or B (blue). The function must return the number of squares in the grid that are finally colored purple, after all sheets have been attached on their given positions.
- Use the function purple to write a function cellophane, that takes the location of a text file as an argument. Each line of this text file contains the description of the position where a cellophane sheet should be attached on a rectangular grid. The first character is a letter that indicates the color (R for red or B for blue) of the sheet. This is followed by four integers that are separated from each other by a single space (not that there is no space between the first letter and the first integer). The integers represent the column and row numbers of the square in the grid that is covered by the top left corner of the sheet, and the width and height of the sheet expressed as a number of squares. The function must return the number of squares in the grid that are finally colored purple, after all sheets have been attached on their given positions.
Example
In the following interactive session, we assume that the file cellophane.txt is located in the current directory. The arrangement of the cellophane sheets on the grid corresponds in both cases to the arrangement in the above figure.
>>> purple([(0, 0, 5, 5, 'R'), (10, 0, 5, 5, 'R'), (3, 2, 9, 2, 'B')]) 8 >>> cellophane('cellophane.txt') 8
Cellofaan is een dunne, transparante film die gemaakt wordt van cellulose. Cellulosevezels van hout, katoen of hennep worden opgelost in een basische oplossing en behandeld met koolstofdisulfide om zo een oplossing te verkrijgen die viscose genoemd wordt. Deze oplossing wordt vervolgens geëxtrudeerd door een spleet in een zuurbad om de viscose terug om te zetten in cellulose.
Cellofaan werd uitgevonden door de Zwitserse chemicus Jacques E. Brandenberger. Hij deed er tien jaar over om zijn transparante films te perfectioneren alvorens er in 1912 een patent voor aan te vragen. Cellulosefilms worden sinds de jaren dertig geproduceerd. Behalve voor het verpakken van voedsel, worden ze ook gebruikt voor een aantal industriële toepassingen zoals het vervaardigen van plakband (waaronder Scotch Tape) en als semipermeabel membraan in bepaalde batterijen. De verkoop van cellofaan is de laatste jaren flink gekelderd vanwege de productie van alternatieve verpakkingsmaterialen, en doordat viscose steeds minder vervaardigd wordt omwille van het vervuilende koolstofdisulfide.
Opgave
Op een vlak oppervlak — bijvoorbeeld een raam of een lichtbak waarop dokters röntgenfoto's bekijken — wordt een rechthoekig rooster aangebracht. Daarvan worden de kolommen van links naar rechts en de rijen van onder naar boven genummerd vanaf nul. Op het oppervlak kunnen rechthoekige cellofaanfilms aangebracht worden, die precies samenvallen met een aantal vlakken van het rooster. Deze transparante films zijn ofwel rood of blauw gekleurd. Indien een vlak bedekt wordt door één of meer rode films dan heeft het een rode kleur. Is een vlak bedekt met één of meer blauwe films, dan heeft het een blauwe kleur. Wanneer een vlak bedekt wordt door minstens één rode en minstens één blauwe film, dan krijgt het een paarsachtige kleur.
Voor gegeven posities van een aantal rode en blauwe films moet je bepalen hoeveel vlakken er paars kleuren. Hiervoor ga je als volgt te werk.
- Schrijf een functie paars waaraan een lijst met de posities van een aantal cellofaanfilms moet doorgegeven worden. Elke film uit de lijst wordt voorgesteld door een tuple met vijf elementen. De eerste twee daarvan zijn natuurlijke getallen die het kolom- en rijnummer van het vlak in het rooster aanduiden dat bedekt wordt door de linkerbovenkant van de film. Daarna volgen nog twee natuurlijke getallen die de breedte en hoogte van de cellofaanfilm aangeven, uitgedrukt als een geheel aantal vlakken. Het laatste element is een string die de kleur van de film aangeeft: R (rood) of B (blauw). De functie moet teruggeven hoeveel vlakken van het rooster uiteindelijk paars kleuren, nadat alle films op de gegeven posities werden aangebracht.
- Gebruik de functie paars om een functie cellofaan te schrijven, waaraan de locatie van een tekstbestand moet doorgegeven worden. Elke regel van dit tekstbestand bevat de omschrijving waar een cellofaanfilm op een rooster moet aangebracht worden. Het eerste karakter is een letter die de kleur (R voor rood of B voor blauw) van de film aangeeft. Daarna volgen vier natuurlijke getallen die telkens van elkaar gescheiden worden door één enkele spatie (let wel, tussen de eerste letter en het eerste getal staat geen spatie). Deze getallen geven achtereenvolgens het kolom- en rijnummer aan van het vlak in het rooster dat door de linkerbovenkant van de film bedekt wordt, en de breedte en hoogte van de film uitgedrukt als een geheel aantal vlakken. De functie moet teruggeven hoeveel vlakken van het rooster uiteindelijk paars kleuren, nadat alle films op de gegeven posities werden aangebracht.
Voorbeeld
Bij onderstaande voorbeeldsessie gaan we ervan uit dat het bestand cellofaan.txt zich in de huidige directory bevindt. De schikking van de cellofaanfilms op het rooster komt in beide gevallen overeen met de afbeelding die hierboven staat.
>>> paars([(0, 0, 5, 5, 'R'), (10, 0, 5, 5, 'R'), (3, 2, 9, 2, 'B')]) 8 >>> cellofaan('cellofaan.txt') 8
| Added by: | Peter Dawyndt |
| Date: | 2013-01-25 |
| Time limit: | 10s |
| Source limit: | 50000B |
| Memory limit: | 1536MB |
| Cluster: | Cube (Intel G860) |
| Languages: | PY_NBC |
| Resource: | None |

 RSS
RSS