| Submit | All submissions | Best solutions | Back to list |
NWERC11B - Bird tree |
Bird tree
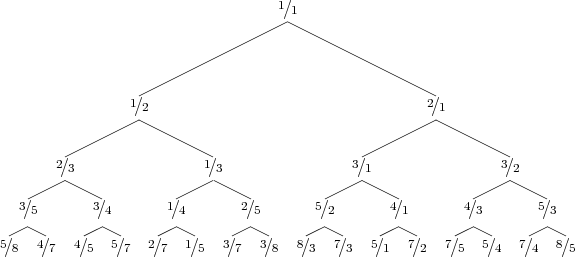
The Bird tree1 is an infinite binary tree, whose first 5 levels look as follows:
It can be defined as follows:
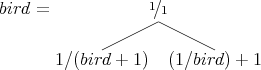
This is a co-recursive definition in which both occurrences of bird refer to the full (infinite) tree. The expression bird + 1 means that 1 is added to every fraction in the tree, and 1∕bird means that every fraction in the tree is inverted (so a∕b becomes b∕a).
Surprisingly, the tree contains every positive rational number exactly once, so every reduced fraction is at a unique place in the tree. Hence, we can also describe a rational number by giving directions (L for left subtree, R for right subtree) in the Bird tree. For example, 2∕5 is represented by LRR. Given a reduced fraction, return a string consisting of L’s and R’s: the directions to locate this fraction from the top of the tree.
Input
On the first line a positive integer: the number of test cases, at most 100. After that per test case:
- one line with two integers a and b (1 ≤ a,b ≤ 109), separated by a ’/’. These represent the numerator and denominator of a reduced fraction. The integers a and b are not both equal to 1, and they satisfy gcd(a,b) = 1.
For every test case the length of the string with directions will be at most 10 000.
Output
Per test case:
- one line with the string representation of the location of this fraction in the Bird tree.
Sample in- and output
|
Input |
Output |
3 1/2 2/5 7/3 |
L LRR RLLR |
1Hinze, R. (2009). The Bird tree. J. Funct. Program., 19:491–508.
| Added by: | Jeroen Bransen |
| Date: | 2011-11-02 |
| Time limit: | 1s |
| Source limit: | 50000B |
| Memory limit: | 1536MB |
| Cluster: | Cube (Intel G860) |
| Languages: | All except: ASM64 |
| Resource: | NWERC 2011 Jury |
hide comments
|
2011-11-28 11:45:25 Jeroen Bransen
The first step is L so we use: 1/(bird' + 1) Then in the subtree bird' we use R, so for that we use the (1/bird) + 1 rule which gives us: 1/(((1/bird'')+1)+1) Finally we are done so here for bird'' we fill in 1/1 and we end with: 1/(((1/(1/1))+1)+1) which is 1/3. |
|
|
2011-11-27 14:42:27 ulasuevoli
i have same doubt as Aseem Kumar .. Clarify it |
|
|
2011-11-27 12:29:19 Aseem Kumar
Can anyone explain how we obtained 1/3 in the LR. Should it not be (1/(1/2) + 1) =3/1 because its parent is 1/2 and using the R rule? |

 RSS
RSS